Gallstones: Treatment Overview
May 16, 2023If you suffer from gallstones, there are surgical and non-surgical treatment options available to help ease your discomfort.
The Inside Rx Blog
Get the Inside Scoop on tips & tricks that may help your family save on prescriptions!
Subscribe to stay up to date with the latest news and tips
Reviewed by the Office of Clinical Evaluation and Policy (OCEP), Evernorth
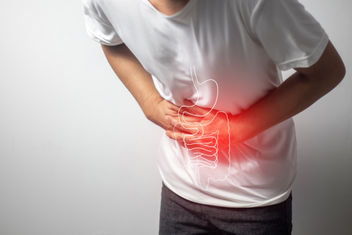
Gallstones are hardened pieces of digestive fluid that can form in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver. These stones are typically made of bilirubin or cholesterol and can vary in size. They may form small, pebble-like stones or larger lumps of concentrated bile content.
Gallstones affect around 10% to 15% of the population, or almost 25 million people, in the United States. Although many types of gallstones resolve without any symptoms or the need for treatment, some people need treatment in the form of medication or surgery.
Continue reading to learn more about the different types of gallstones treatment.
Diagnosis of Gallstones
Most gallstones do not cause any symptoms and are often discovered incidentally during imaging tests for unrelated conditions. As a result, a diagnosis for gallstones typically occurs when symptoms are present.
Symptoms arising from gallstones are usually due to blockage or inflammation. Gallstones can completely block the bile duct, which carries digestive juices and bile from the liver to the first part of the small intestine (duodenum) for digestion. Left untreated, gallstones can lead to inflammation of the gallbladder, bile duct and pancreas.
Gallstones that cause blockage or inflammation may result in symptoms such as:
- Sudden and intensifying pain in the upper right portion of your abdomen
- Pain in the center of your abdomen, just below the breastbone
- Back pain between the shoulder blades
- Pain in the right shoulder
- Nausea or vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
If you experience any of these symptoms, a healthcare provider may use the following tests to diagnose gallstones:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, MRCP or HIDA scan
- Blood tests
Surgical Gallstones Treatment Options
Unless gallstones are causing symptoms, a healthcare provider may recommend monitoring the condition. If you experience symptoms of gallstones, then surgical removal of the gallbladder is often recommended. Surgical treatment options for gallstones include:
Cholecystectomy
A cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder, and there are two main types: laparoscopic and open. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, a minimally invasive surgery, is the most common treatment for symptomatic gallstones. It involves the removal of the gallbladder through small incisions in the abdomen, offering a shorter recovery time than open surgery.
However, in cases where laparoscopic surgery isn't possible, an open cholecystectomy may be performed. This approach requires a larger incision in the abdomen to remove the gallbladder and typically involves a longer hospital stay.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
ERCP is a procedure that combines endoscopy and X-ray imaging to find and remove gallstones lodged in the bile ducts, gallbladder or pancreas. The procedure involves removing the stones with the aid of an endoscope, a long flexible tube that may be entered through the mouth.
Non-Surgical Gallstones Treatment Options
Although surgical options are the primary way to treat gallstones, there are non-surgical methods such as medications. Sometimes, gallstones that are small enough may pass through the gallbladder on their own without any symptoms. Other options include:
Medications
Healthcare providers may prescribe medications to help dissolve gallstones. These drugs, such as ursodiol and chenodiol, work by reducing the amount of cholesterol in bile. However, it may take months for medications to get rid of gallstones, and may be ineffective in some cases. As a result, they’re a secondary option to surgical methods.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage gallstone symptoms and prevent their recurrence. These changes include:
- Eating a low-fat diet
- Increasing fiber intake
- Drinking plenty of water
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- If losing weight, avoid rapid weight loss
- Limiting high-cholesterol foods
If you have a family history or other risk factors for gallstones, regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help detect any complications from gallstones early. It’s important to monitor for recurring symptoms and maintain a healthy lifestyle to treat and prevent gallstones.
Choosing the Right Treatment Option
It’s always best to consult a healthcare provider to determine the right gallstone treatment option for you. If you suspect that you have gallstones or are experiencing symptoms related to gallstones, consult your healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Early diagnosis and intervention can help prevent complications and ensure the best outcomes for your health.
Sources:



