Pain and Inflammation: Treatment Overview
June 14, 2022Pain and inflammation are quite common among American adults and can become a nuisance to deal with. Luckily, there are a number of treatment options available to reduce or manage symptoms.
The Inside Rx Blog
Get the Inside Scoop on tips & tricks that may help your family save on prescriptions!
Subscribe to stay up to date with the latest news and tips
Reviewed by the Office of Clinical Evaluation and Policy (OCEP), Evernorth
Approximately 20% of adults in the United States experience pain on most days of the week. Pain can be caused by inflammation from injuries, such as injuries of the back, or medical conditions, such as arthritis. Although pain can be difficult to live with, there are treatments available to help manage pain. These include both drug and non-drug treatments.
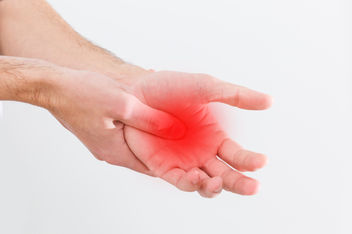
Signs of Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s way of dealing with an injury or damage to the body. After an injury, for example, the immune system starts an acute inflammatory response to heal injured tissues. Inflammation can also be chronic. Chronic inflammation from rheumatoid arthritis is caused by an overactive immune system. Signs and symptoms of inflammation may include:
- Pain: This is caused by inflammatory chemicals that stimulate nerve endings, causing the affected areas to feel more sensitive.
- Swelling: This is caused by what’s known as edema, or a build-up of fluids at the affected site.
- Heat: An increase in blood flow to the affected area can cause the area to feel warm when touched.
- Redness: This is another result of increased blood supply to the area of injury.
- Reduced/Loss of function: Difficulty moving the area.

Why Drug Prices Change and How Discount Cards Help

How to Handle a Drug Price Increase (After Your Plan Resets)

Preparing for 2026: Prescription Savings Trends & Planning Tips

Tips for Staying Healthy During Holiday Travel
Types of Pain
There are two main types of pain: acute and chronic.
- Acute pain usually comes on suddenly, because of a disease, injury, or inflammation. It can often be diagnosed and treated. It usually goes away (within 4 weeks), though sometimes it can turn into chronic pain.
- Chronic pain lasts for a long time (beyond 3 months), and may cause severe problems. Chronic inflammation can be one cause of chronic pain.
Treatments for pain and inflammation
Pain is not always curable, but there are many ways to alleviate it. Treatment depends on the cause and type of pain. Non-drug treatments, such as physical therapy, acupuncture and meditation, and drug treatments, such as pain relievers, are effective options for treating pain and inflammation.
Everyone experiences pain and responds to treatments differently. As always, it’s best to consult with your doctor to understand the best treatment options for your situation.
Non-drug treatments
Non-drug treatments are often preferred and recommended first before trying a medication to relieve pain. These include natural methods to help manage pain.
Physical therapy can improve your mobility and flexibility, as well as your ability to carry out daily activities. It includes various techniques, such as massage, manipulation, and other movement-based therapies. Physical therapists can give you advice and guidance on what type of therapy may benefit you.
Acupuncture is a type of therapy that uses very thin needles to stimulate certain points of the body. It is an ancient Chinese-based treatment that is based on the idea of qi, or energy, flowing through the body. Practitioners of acupuncture believe that rebalancing the qi is vital to support the body’s healing processes, and research suggests that acupuncture is effective for chronic pain.
Meditation involves awareness training, acceptance of the present moment, and physical relaxation. There are different techniques to practice meditation, including focusing on the breath and visualizing positive imagery. Strong evidence suggests that meditation may help improve pain and quality of life.
Other non-drug treatments are available. In severe cases, surgery may be required to treat more serious problems.
Consult your doctor to discuss which non-drug treatments are a good fit for you.
Drug treatments
Using over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers can be an effective way to alleviate mild to moderate pain.
OTC non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often used for minor aches, pains, and pain associated with inflammation. OTC NSAIDs include aspirin, naproxen and ibuprofen. NSAIDs work to reduce pain by blocking certain inflammatory substances in the body. Therefore, aspirin, naproxen and ibuprofen are good pain reliever options for those who have pain associated with inflammation.
Another example of an effective OTC pain reliever is acetaminophen. It is not an anti-inflammatory but it is a good option for patients unable to take NSAIDs for relief of their minor aches and pains.
Due to potential risks or side effects, it is important to always follow the guidance of your doctor (or pharmacist), and use pain relievers according to the dosing instructions.
If needed, your doctor may prescribe a more powerful, prescription pain reliever.
Talk to your doctor
Now that you know some of the most effective ways to manage pain associated with inflammation, you can make informed decisions about what is best for you. Before choosing the right treatment and management strategies, it is important to consult your doctor for guidance. Always follow their advice and take medication according to instructions.